-Teeth develop months before the arrival of the child
-Eat foods rich in calcium, phosphorous, vitamin C, Vitamin D during pregnancy
-Do not take tetracycline medicine during pregnancy
-Teeth may be the hardest part of the human body, it’s not drink opener.
-Teeth are not bone
-Teeth change to adjust to human body needs
-Do not use teething tablet/ gel with benzocaine
-Brush your teeth & child’s with age-appropriate tooth brush and fluoride tooth paste
-Brush twice a day.
-make dental appointment for your baby after the eruption of the first tooth
Your child teeth formation starts as early as 6 weeks of conception of the child in your tommy. Your nutrition during pregnancy determines the child teeth substance. Good nutrition from the mother during pregnancy is important in the development of the teeth.
The mother’s diet should have adequate amounts of calcium, phosphorus, vitamin C, and vitamin D. Certain medicines, such as tetracycline, should not be taken by the mother while she is pregnant because it can cause discoloration to the developing teeth of the embryo
Just as the milestones mark the various stages of a child’s physical and emotional development, the eruption of teeth marks the oral and dental development of a child.
. There are 4 main phases of development of the tooth:
- The first stage begins in the fetus at about 6 weeks of age. This is when the basic substance of the tooth forms.
- Next, the hard tissue that surrounds the teeth is formed, around 3 to 4 months of gestation.
- After the child is born, the next stage occurs when the tooth actually protrudes through the gum.
- Finally, there is the loss of the primary “baby” teeth.
Teeth Fact
A very interesting fact about the teeth is that though they don’t come physical with the body at birth, the basic teeth substance has been developed months before the arrival of the child. And they live longer than the body because teeth contain the hardest substance in the human body.
The teeth can make a person look ugly or beautiful. Teeth can add value to the radiance on the face. Teeth can make your smiles warmer.
The importance of teeth in the human lives cannot be overemphasized. Without teeth, eating which provides the body the micro and macro nutrients, becomes a challenge. Toothless mouth, like a toothless dog that cannot bite, will be lacking in shape & sharpness and can result in taunted growth for the person.
The teeth are special organs in the human body. Even though they share some features (constituents and appearance) with the bone, they are however not bone. The tooth has 3 layers; the outer layer (enamel) which happen to be the hardest substance in the human body, the middle layer (dentine) and the inner layer (pulp). The enamel and dentine do not contain blood vessels and nerve thus, they do not have sensation of their own. The pulp contains blood vessels and nerves.
The teeth are not usually present at birth except in cases of natal tooth which is present at birth or neonatal tooth which erupts just after birth before the usual eruption dates. The precursor of both the baby and adult teeth are already formed during the development of the fetus.
TYPES OF TEETH:
There are four (4) types of teeth.
- Incisor: They are located in front of both the upper and lower jaws. They are further divided into central and lateral incisor depending on their exact location. There are 4 each on upper and lower jaw in both the primary and permanent dentition. They are used to cut food.
- Canine: they are located next to the incisor. There are 2 on upper and lower jaw in both primary and permanent dentition. They used to tear food.
- Premolars: They are seen in permanent dentition only. They are located before the molars. There are 4 on each jaw. They are used to crush food.
- Molar: Located at the back of the jaw. There are 4 on each jaw in the deciduous dentition and 6 on each jaw in the permanent dentition. They are used to grind food.
SET OF TEETH:
There are 2 sets of teeth seen in human being. They are present at different stages of the human life. The change is important to adjust to the need of the human body as it undergoes growth and development. The two sets are
- Primary, Baby or Deciduous teeth: These set of teeth are seen in the early part of the human life (between 6 months to 14 years). They are fewer in number (20) and generally smaller in size than the permanent teeth. They appear whiter too. The table below shows the eruption and shedding dates for the primary teeth:
UPPER JAW
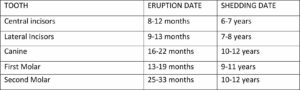
LOWER JAW
• PERMANENT (SECONDARY) TEETH: These set of teeth are seen later on in life. They are 32 in number, 12 more than the primary dentition. They are quite larger than the primary dentition. This is to adjust to the feeding pattern seen in adults. Eruption dates for the adult dentition are listed below
UPPER JAW
LOWER JAW
There is a wide range of variability of when a first tooth may appear—some babies may not have any teeth by their first birthday! So, no panic when your baby does delay. But when the delay is unreasonably prolonged consult teeth specialized doctor.
FUNCTION OF TEETH:
Function of the teeth include
- Feeding: The teeth is used to tear, cut, crush and grind food. This aids easy swallowing and digestion of the food.
- Aesthetics: The teeth contribute to the appearance and beauty of the face.
- Phonation: The teeth is essential in the pronunciation of some letters and words
Common teeth problems:
There are numerous problems or disease affecting the teeth but we will focus on the common ones.
- Caries: It simply means hole on the tooth. This is the leading cause of toothache in human being. The hole is as result of decay of the tooth structure. It is initially painless but becomes painful when the hole reaches the pulp.
- Periodontitis: this means the inflammation of the surrounding structures of the teeth. Caused by long term accumulation of plaque and dirt around the teeth. The tooth becomes painful and mobile after some time.
- Fracture: this can range from just a chip to frank breakage of the tooth. It is usually as a result of assault, accident or habits like using the tooth as a tool to open drinks or break hard substances.
- Ulcer: this refers too wounds or breakage in the continuity of the surface of the gum and mucosa of the mouth. It could be as result burn by chemicals and hot substance or by physical cut by the teeth or other objects.
- Teething: ‘teething’ is the process of erupting or bringing forth teeth. This period is usually associated with symptoms like fever and stooling. Teething itself is not a sickness. The gum in relation to the area where a tooth is erupting is always itching, in an attempt to ease the itch, children put whatever is available in the mouth. This, coupled with the less developed immune system of the child predisposes them to infection with can then cause those symptoms
Avoiding the problems
The above listed problems can be avoided to a large extent if proper oral hygiene practices are maintained. The oral hygiene practices include:
- Brushing at least twice in a day with age-appropriate toothbrush and fluoride containing tooth paste. There should be no feeding whatsoever after the last brushing for the day
- Flossing in between the teeth with a floss rather than using a tooth pick.
- Replace your tooth brush once every three months or as soon as the bristles wither.
- Limit intake of refined carbohydrates and sugary foods and drinks.
- Limiting use of alcohol and total abstinence from tobacco.
- Regular visit to Dentist for examination and professional washing (Scaling and Polishing), at least twice in a year.
The teeth are needed all through life to ensure functions like feeding, aesthetics and speaking which in turn help improve quality of life. It is important to keep them healthy by maintaining good oral hygiene at all times.